Customer Experience Management in the Digital Age
Customer Experience Management CXM is a critical driver of growth and profitability. As technology continues to transform how companies interact with their customers, the role of CXM has become more complex and vital than ever.
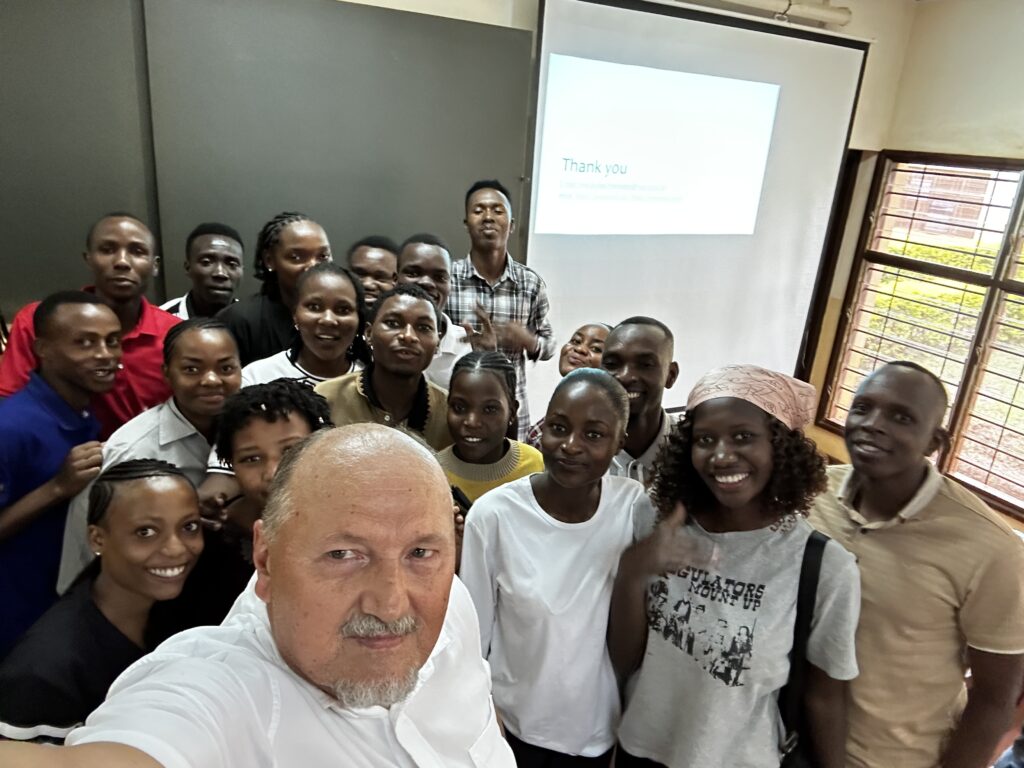
This blog post explores the key concepts, strategies, and tools involved in managing Customer Experience CX in the digital age, drawing insights from the presentation by Mieczysław Pawłowski, PhD. You can download it from here below.
Customer Experience Management in the Digital Age – Navigating the New Frontier.
The Evolution from CRM to CXM
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) has long been a cornerstone of business strategy, focusing on understanding and influencing customer behavior to drive acquisition, retention, loyalty, and profitability.
Digital technologies have advanced, the scope of Customer Relationship Management CRM has expanded to Customer Experience Management CXM. CXM goes beyond traditional CRM by integrating digital tools and strategies to enhance every touchpoint a customer has with a business.
Thank you to Tanzania’s students for listening to me with attention and all activity I experienced from YOU.
The Role of CXM in Business Growth
Effective CXM is crucial for business growth, as it directly impacts customer satisfaction, loyalty, and overall profitability. Companies that excel in CXM can differentiate themselves in the market, build stronger relationships with their customers, and drive sustainable growth. The process involves several key components:
- Customer Knowledge: Collecting and analyzing customer data to understand their characteristics, needs, and preferences.
- Value Creation: Linking organizational strategy with customer management processes to create value for both the company and the customer.
- Competitiveness: Combining business processes and technologies to differentiate products and services in the market.
CXM in the Digital Age
The digital age has brought significant changes to CXM, with e-commerce, digital marketing, and omnichannel sales becoming integral parts of the customer journey. Businesses must now operate and interact with customers differently, utilizing digital interfaces and tools to enhance the customer experience. Key trends in CXM include:
- Digital Transformation: Companies must adapt to digital technologies to stay competitive and meet customer expectations.
- Digitization of Customer Interactions: The integration of digital technologies into customer interactions has evolved from basic processes like online ordering to a complete digitization of the customer journey.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Businesses are shifting from a product-centric to a customer-centric approach, placing customer experience at the forefront of their interactions.
About digital age you can read here: What is digital age?
The Profession of Customer Experience Management
As CXM becomes increasingly important, the role of the Customer Experience Manager has emerged as a critical profession. These professionals are responsible for optimizing every touchpoint a customer has with a business to build brand loyalty and enhance customer relationships. Common responsibilities of a Customer Experience Manager include:
- Championing opportunities to improve the customer experience.
- Driving customer retention and satisfaction.
- Mapping the customer journey and identifying opportunities for proactive intervention.
- Guiding teams in effective client issue resolution.
- Developing strategies for continuous improvement.

Strategies for Effective CXM
To succeed in CXM, businesses must adopt strategies that align with their goals and market position. Some effective strategies include:
- Market Leader: Treating customers as regular resources and focusing on customer satisfaction.
- Pretender: Using customer feedback to improve and innovate.
- Niche: Differentiating through quality and specialized offerings.
- Price Leader: Focusing on product value and competitive pricing.
The Impact of Technology on Customer Experience
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping customer experience in the digital age. From self-service kiosks that boost consumer spending to digital interfaces that streamline customer interactions, technology enhances the overall customer experience by providing convenience, personalization, and efficiency. Key technological impacts include:
- Enhanced User Experience: Visual displays and photography help entice customers and upsell options.
- Data Collection: Detailed data on customer preferences allows for precise targeting and improved service.
- Automation: Automating processes like checkout frees up staff time and enhances customer satisfaction.
Customer Experience vs. Service Quality
The search results strongly suggest that while “Service Quality” is the foundational academic concept, “Customer Experience” (CX) is the current industry and high-level curriculum trend.
1. CX is the Dominant Industry and Advanced Curriculum Term 🚀
The term “Customer Experience” (or “CX”) is now the preferred term in executive education and advanced programs:
- Masters Programs: Top business schools (like IE Business School, MSU Broad College of Business, Rutgers, HBS Online) offer entire programs or executive courses dedicated to “Customer Experience Management” or “Transforming Customer Experiences.” (Source 3.1, 3.3, 3.4, 3.6). This demonstrates that, for students interested in advanced studies, CX is a recognized, specialized field.
- CX is Strategic: CX is consistently described as a “leading strategy companies harness to grow their market share” and a source of “long-term competitive advantage.” (Source 3.2, 2.5). Business leaders are recognizing that CX is crucial.
- CX is a Modern Evolution: Scholars note that services are undergoing a transformation from the traditional concept of a service transaction to one of an “experience” (Source 1.1). CX is seen as the latest evolution that surpasses simple products and services.
2. Service Quality is the Academic Foundation (The “Known” Term) 🎓
Students are likely more familiar with “Service Quality” because it is the cornerstone of early marketing and management theory:
- Service Quality is the Antecedent: The research confirms that Service Quality (SQ) is viewed as the fundamental antecedent or predictor of Customer Experience (CX) (Source 1.3). In academic models, improving Service Quality is a way to achieve positive Customer Experiences.
- Student Experience Studies: Studies assessing student satisfaction in higher education often use Service Quality models (like SERVQUAL) as the primary framework, although they are now explicitly linking SQ results to overall Customer Experience (Source 1.1, 1.6).
Service Quality – The gap between customer expectations and perceptions of service delivery. Academic, Tactical. It focuses on a transactional evaluation of reliability, responsiveness, etc. It signals a foundational, measurement-focused course.
Customer Experience – The customer’s overall perception and internal, subjective reaction to every direct or indirect contact over a period of time. Strategic, Holistic. It focuses on the full journey and emotional connection, making it a more complex, managerial, and future-oriented topic.
The term “Client” vs. “Customer” is a minor issue. In modern business and academic literature (including the high-level Master’s programs cited), “Customer” is the standard term used in the context of CX, as it refers to a broader B2C or B2B user, not just a high-value client.
Customer Experience Management is the title most aligned with advanced, strategic business education, which attracts the type of student who wants to be on the cutting edge and those seeking high-value skills.
Customer Experience can be combined with the analytical, digital, or process-oriented keywords suggested previously to make its content clear and appealing to the strongest cohorts
Conclusion
Customer Experience Management is not only essential for business growth but also a strategic priority for companies aiming to differentiate themselves in the market. By investing in CXM, businesses can drive increased profitability, customer loyalty, and brand strength while reducing costs and enabling continuous improvement. As the digital age continues to evolve, the importance of CXM will only grow, making it a critical area of focus for businesses looking to thrive in the modern economy.
In conclusion, the role of CXM in the digital age is multifaceted and ever-evolving. By continuously developing strategies, leveraging technology, and prioritizing customer satisfaction, businesses can ensure they remain competitive and successful. The future of CXM is bright, and with the right approach, companies can create unforgettable experiences that drive long-term growth and loyalty.
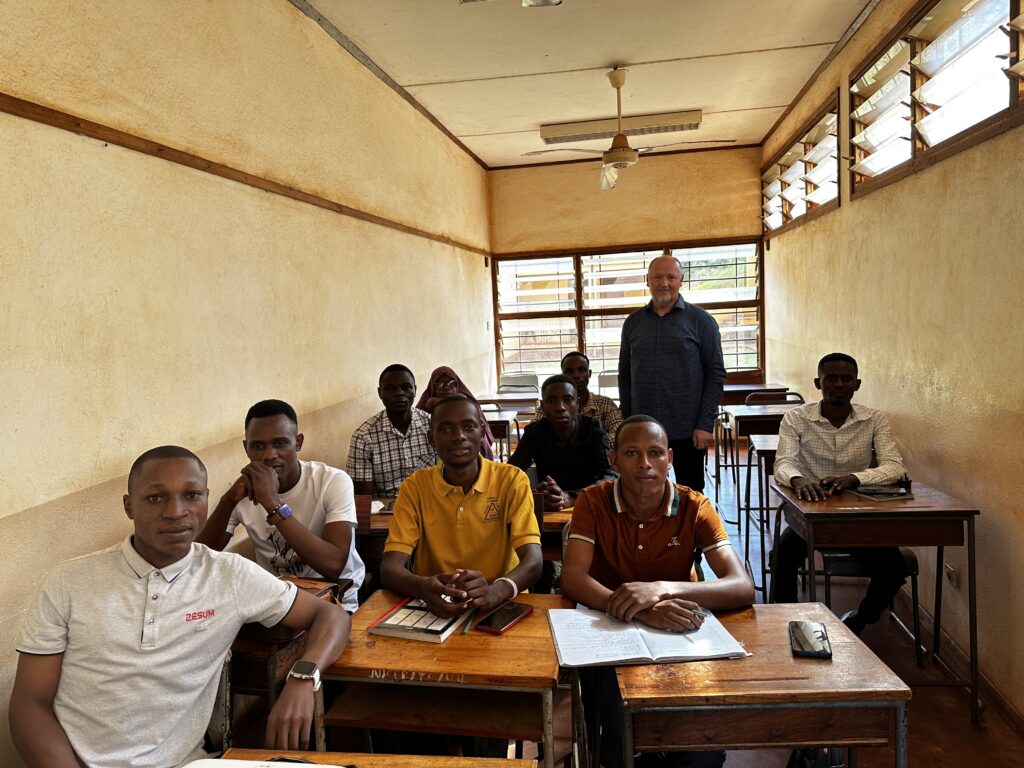
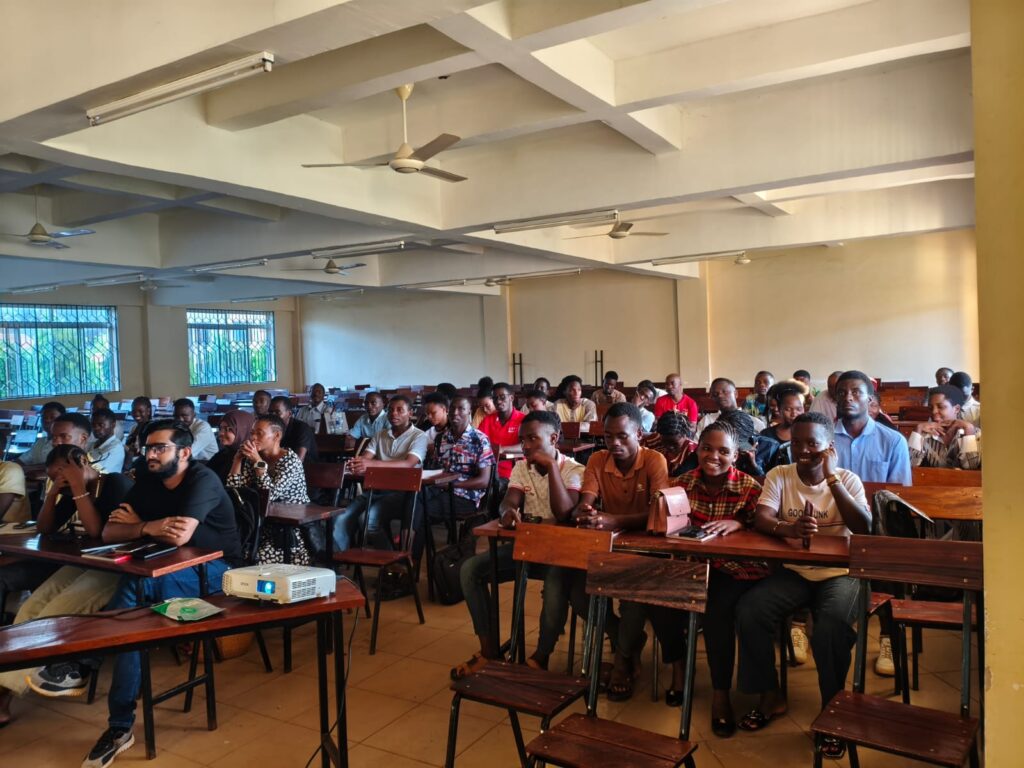
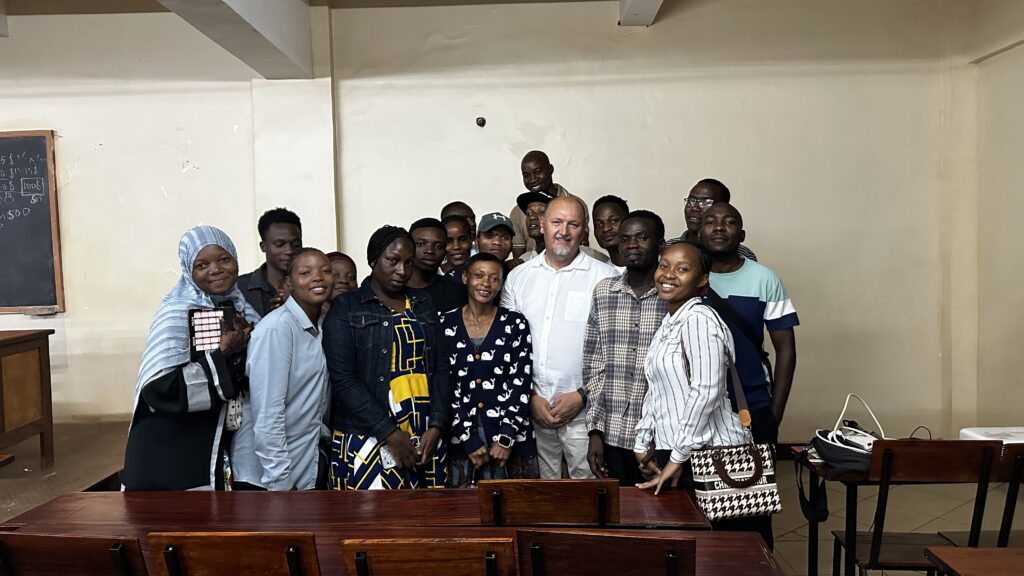















One Comment
Comments are closed.