Blockchain Sustainability
Blockchain Sustainability is the relationship between blockchain and sustainability has evolved a lot in recent years. It is a fascinating topic, as it shows how a technology, that has raised quite a few concerns on the environmental impact front, is becoming one of the greatest allies of sustainability, both environmentally and socially. This is not only at the level of the individual organization but also at the level of the supply chain and the entire economic system.
Definition and Basic Principles of Blockchain
Blockchain is a shared, immutable digital ledger, enabling the recording of transactions and the tracking of assets within a business network and providing a single source of truth. Blockchain uses the three principles of cryptography, decentralization, and consensus to create a highly secure underlying software system that is nearly impossible to tamper with. There is no single point of failure, and a single user cannot change the transaction records. Blockchain Sustainability.
The Role of Blockchain in Sustainability
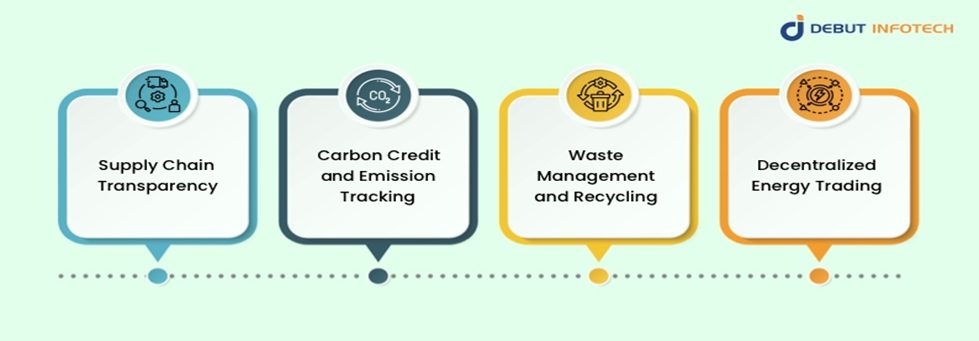
Blockchain technology and sustainability have many commonalities, one of which is the need to make environmental programs as transparent and efficient as possible. Leveraging blockchain enables businesses to monitor and validate sustainable activities, therefore reducing fraud and improving corporate social responsibility. Some of blockchain’s main functions in sustainability are:
1. Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain guarantees a totally visible operation of supply chains. By using an immutable ledger, businesses can document every phase of a product’s cycle, enabling consumers and stakeholders to check ethical sourcing, fair labor standards, and environmentally friendly manufacturing procedures.
2. Carbon Credit and Emission Tracking
Blockchain tracks emissions in an auditable, tamper-proof manner, which allows precise carbon credit accounting. This guarantees adherence to international environmental criteria and enables companies and governments to track their carbon offset initiatives. Blockchain Sustainability.
3. Waste Management and Recycling
By offering digital tokens in return for getting rid of trash, smart contracts on blockchain platforms can encourage recycling programs. These automated solutions lower landfill overflow, track waste better, and support circular economy projects.
4. Decentralized Energy Trading
With blockchain technology, businesses and people may bypass middlemen and sell excess renewable energy directly. This helps to spread green energy effectively and pushes the acceptance of sustainable power sources. Blockchain Sustainability.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain for Sustainability
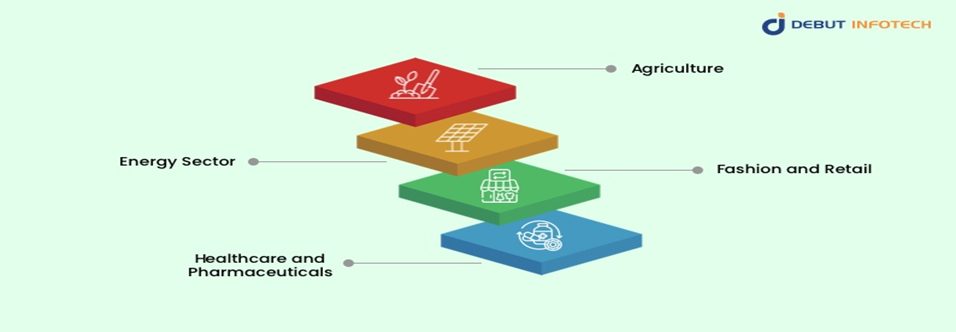
1. Agriculture
Blockchain systems track agricultural supply chains, guarantee fair trade, help lower food waste, and support sustainable farming methods. They also help companies like IBM Food Trust to increase food industry traceability. Blockchain Sustainability.
2. Energy Sector
Companies in the energy sector are using blockchain technology to create decentralized energy networks. These networks allow for transparent renewable energy certifications and peer-to-peer energy trade. Platforms such as Power Ledger and We Power make blockchain-based energy trading possible. Tesla’s Virtual Power Plant.
3. Fashion and Retail
Blockchain is used by luxury businesses and fashion stores to confirm ethical procurement and cut fake goods. Consumers can scan QR codes to check products’ sustainability credentials and authenticity.
4. Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Blockchain tracks the source of raw materials, lowers waste, and guarantees responsible disposal of outdated medications, therefore guaranteeing that medical supply chains follow ethical and environmental rules. Blockchain Sustainability.
Challenges and Limitations
Blockchain technology still faces important sustainability limitations, especially due to the high energy use of certain models like Proof of Work, which require large amounts of electricity and generate significant environmental impact. It also struggles with scalability, as many blockchains cannot process high transaction volumes quickly or efficiently enough to support real-time applications such as detailed supply-chain tracking. In addition, governance challenges in decentralized networks make it difficult to ensure fair decision-making, ethical practices, and equal participation among users. These issues show that while blockchain has strong potential, it still needs improvements in energy efficiency, scaling methods, and governance structures to be truly sustainable.
Future of Blockchain in Sustainability
Although its future is uncertain, blockchain shows great promise for sustainability. As technology develops, blockchain systems are expected to become more scalable, energy-efficient, and widely adopted in sustainability projects. Key trends include the shift toward green blockchain protocols, integration with IoT and AI for better monitoring of sustainability metrics, increased corporate responsibility to meet ESG goals, and stronger collaboration between governments and businesses to create supportive regulations.
Conclusion
Blockchain is transforming sustainable business with improved transparency across different areas. This includes supply chains, energy, and finance. It tracks products from source to consumer, verifies carbon credits, and supports renewable energy trading.
All in all, it reduces fraud, lowers emissions, and promotes ethical practices. So, if you haven’t started using these advances, now is the time to adopt blockchain for sustainability. Act today and build a greener, more transparent future with blockchain.